1.0 Introduction
1.1 Current Automation Pyramid
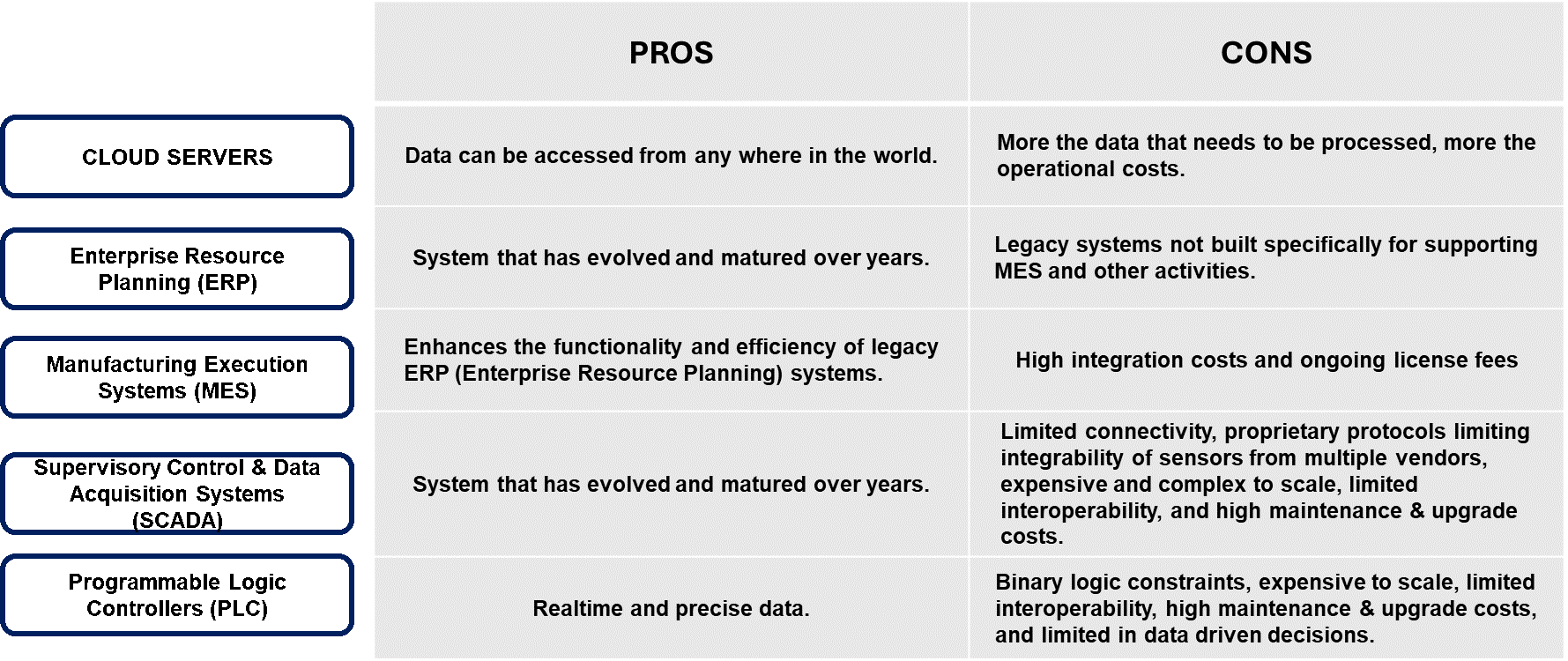
Most industries today rely on Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)-based automation. PLCs receive data from sensors and based on their programmed logic, send commands to output devices like actuators to perform actions, such as starting or stopping specific machines.
The next layer in PLC systems is SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), which operates through centralized software. SCADA collects data from multiple PLCs across a facility and visually displays this information for operators to monitor and control operations efficiently.
Above SCADA lies the Manufacturing Execution System (MES), a separate platform designed for production management. SCADA systems provide real-time shop floor data to MES platforms, which process this data to deliver actionable insights, such as identifying bottlenecks or calculating Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE). For optimal integration, MES and SCADA systems from the same vendor enable MES to send commands back to SCADA, facilitating adjustments to machine operations in line with production requirements.
At the apex of the pyramid is the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. ERP handles business-level functions, such as tracking customer orders, monitoring raw material availability, assessing production status, generating reports, and enabling material procurement. From a business management perspective, ERP acts as the organization's brain, using production data from MES to ensure smooth transitions from inventory management to production and delivery.
Simply put, if you look at this process top down:
- ERP: Focuses business level activities such as demand, supply, and inventory management.
- MES: Manages and optimizes production processes, including scheduling, resource allocation, and quality control, using data from SCADA systems.
- SCADA: Provides live shop floor data and ensures operational smoothness, aligned with MES directives.
- PLC: Captures real-time data from sensors deployed on the shop floor, executes actions based on its predefined program logic, and communicates this information to the SCADA system for centralized monitoring and control.
Although PLC-based automation systems have been pivotal in advancing industrial operations since the 1990s, they are not without limitations. Over time, evolving requirements and technological advancements have exposed several gaps and challenges that must be addressed to meet today's industrial demands.
Traditional PLC/SCADA systems, while foundational in industrial automation, face limitations in adaptability and precision, primarily due to their binary logic (YES/NO outputs). These constraints hinder proactive planning and decision-making in scenarios requiring nuanced variability, such as temperature monitoring. As operations scale, these limitations compound, reducing the usability of data for actionable insights.
Upgrading to smart monitoring systems with advanced sensors, edge computing, and AI-driven analytics offers a transformative solution. These systems enable predictive maintenance, real-time insights, and flexible responses to dynamic variables, ensuring operational efficiency, enhanced equipment longevity, and data-driven decision-making aligned with modern industrial demands.
1.2 Trending and Upcoming Automation Pyramid
Industry 4.0 standards are the buzz words across all industries these days and one can wonder whether meeting such standards is possible giving the current state of operations. So, let’s look at where you are first.
- Industry 1.0 Standard: Mechanized mass production instead of handmade production. So, yes, you have already crossed Industry 1.0 milestone.
- Industry 2.0 Standard: Mechanized mass production on multiple assembly lines using electricity instead of steam power and centralized production line. So, again, yes, you have already crossed Industry 2.0 milestone.
- Industry 2.5 Standard: Not officially recognized, but used to describe the transition between Industry 2.0 and 3.0. Since you use electromechanical systems with relays, timers, and HMIs, you are Industry 2.5 compliant.
- Industry 3.0 Standard: Focuses on digital communication and automation. If you’re using PLCs and other standardized processes, you are near Industry 3.0 readiness but need a final push to get there fully.
- Industry 4.0 Standard: Emphasizes advanced technologies like IoT, AI, big data, and robotics. It supports seamless communication, automation, and efficiency across systems.
Key elements of Industry 4.0 include:
- Interconnectivity: M2M (Machine to Machine) and H2M (Human to Machine) communications via IoT and industrial internet protocols.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Big data analytics for monitoring, optimization, and prediction.
- Interoperability: Common standards to allow different systems to work together seamlessly.
- Cyber Security: Protocols to secure connected systems.
- Other upgrades: Robotics, digital twins, and sustainable technologies.
To reach Industry 4.0, the final missing piece in your 2.75-ready setup is data digitization. Once complete, stepwise enhancements can bring you into full Industry 4.0 compliance. This is not easily done using traditional PLCs—enter IoT. IoT-based systems are more cost-effective and modular, offering better insights and flexibility compared to existing PLC-only architectures.
Plus, terms like Total Preventive Maintenance (TPM) and Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) are built into the Industry 4.0 framework, making the transition not just viable, but valuable.
All you need to consider at this point is to implement Internet of Things (IoT) devices and complete the Data Digitization step to quickly move forward towards Industry 4.0 readiness!
2.0 A Phased Approach to Maximize Results
Adopting a layered approach empowers you to establish clear, measurable goals while streamlining the process of upgrading your facilities. Beyond the convenience, this strategy allows you to prioritize objectives based on your unique needs. While every customer has their own set of priorities, here’s the thoughtfully crafted, step-by-step approach we recommend.
2.1 Phase #1: Digitize your Safety Setup
Protecting personnel and equipment is paramount, as even minor lapses in safety measures can lead to devastating outcomes. While regulatory requirements mandate certain provisions, they often leave critical gaps that can result in severe consequences. For example, depending solely on periodic thermography-based phase line temperature monitoring can inadvertently heighten the risk of electric contact-related fire incidents. Similarly, random placement of smoke detectors coupled with reliance on audible alarms can significantly delay emergency responses during fires. However, these vulnerabilities can be seamlessly addressed with advanced, proactive solutions. In-line wire temperature monitors offer continuous, real-time monitoring, reducing the likelihood of undetected hazards. Meanwhile, mesh-networked smoke detectors go beyond localized alarms—alerting remote locations and integrating with management systems to enable swift, coordinated responses to potential dangers. By embracing these smart solutions, you can eliminate risks effectively, protect your investments, and ensure unparalleled peace of mind.
2.2 Phase #2: Digitize your Power Monitoring System
Optimizing cost-effective operations is the natural next step in driving efficiency and profitability. With multiple machines on the shop floor, along with facilities like air conditioners and air handling units, it's crucial to adopt a data-driven approach to energy management. By monitoring the power consumption of individual equipment and comparing it to the cumulative input consumption, you unlock valuable insights into Original Equipment Efficiency (OEE) which is a key performance metric used to evaluate how effectively equipment is utilized. This analysis not only highlights opportunities to enhance efficiency but also reveals hidden issues, such as aging wiring or machinery, that could otherwise go unnoticed. Beyond diagnostics, this data serves as the foundation for actionable strategies to reduce energy consumption and cut costs, empowering you to make informed, impactful decisions for a smarter and more sustainable operation.
2.3 Phase #3: Implement Light Management System
Adequate lighting is fundamental in any workshop or stockroom to ensure productivity and safety. However, traditional lighting systems can significantly inflate operational costs. The integration of daylight harvesting and motion sensor networks presents a transformative solution. By leveraging natural light in general work areas and deploying motion sensors in warehouses and stockrooms, overall power consumption can be reduced by an impressive 30% to 60%. In spaces with access to natural light, implementing systems that automatically adjust light intensity can significantly reduce power consumption while maintaining a comfortable working environment. By optimizing daylight harvesting, these systems intelligently complement natural light, minimizing unnecessary energy usage. In areas such as warehouses and stockrooms, where occupancy is intermittent, deploying motion sensors presents an invaluable solution. These sensors ensure lights are activated only when needed, drastically reducing energy wastage. This not only curtails operational costs but also promotes sustainability. In addition, ALMS (Advanced Lighting Management System) not only lowers energy expenses but also provides a maintenance-friendly experience. Advanced lighting systems facilitate fault identification and remote monitoring, streamlining management processes and minimizing downtime. Furthermore, implementing smart lighting can extend the life span of lighting fixtures. By automatically adjusting internal parameters, such as temperature, smart lights optimize performance and durability, delivering long-term value for your investment. Investing in intelligent lighting solutions represents an opportunity to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and operational cost-effectiveness, ensuring your workplace stays ahead of the curve.
2.4 Phase #4: Unlocking New Levels of Operational Efficiency
With phases 1 to 3 already achieving over 90% digitization of your workshop, the next logical step is to implement customized solutions tailored to your specific operational needs. Key additions to consider in this phase include: 1. Enhancing Data Collection with Additional Sensors: Equip machinery with supplementary sensors to capture crucial parameters for more informed and data-driven decision-making. 2. Implementing Edge Computing: Introduce an edge-computer to your workshop, enabling localized data storage and calculations. This ensures efficient processing and real-time display of desired metrics. 3. Seamless System Integration: Integrate the edge computing system with your existing measurement, monitoring, and control systems to create a unified and comprehensive overview. By advancing to Phase 4, you can shift your focus to strategic initiatives like:
Total Preventive Maintenance (TPM)
With all machinery, workshop safety equipment, lighting systems, and other essential components now digitized and connected through a workshop-specific edge computing system, you gain the ability to receive proactive maintenance alerts the moment fault conditions begin to surface. These include issues such as a loose motor belt, elevated phase line temperatures, or lighting failures. Such action-oriented notifications enable timely intervention to identify and address potential problems before they escalate, minimizing downtime and preventing costly disruptions. This streamlined approach to predictive maintenance ensures operational efficiency, enhances equipment reliability, and safeguards workplace productivity.
Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE)
The integration of a Power Management Layer with Total Preventive Maintenance (TPM) enables the collection of precise and actionable real-time data, such as machine availability and performance metrics. When this data is combined with Quality Metrics, organizations can achieve significant improvements in productivity while simultaneously reducing rework and minimizing wastage. This cohesive approach ensures that operations are optimized across multiple dimensions, empowering stakeholders to identify inefficiencies, implement corrective actions proactively, and maintain consistent quality standards. By leveraging these interconnected systems, businesses can drive sustained efficiency and enhance overall profitability.
Scalable and Efficient Transition to Industry 4.0
This approach can be strategically implemented on a workshop-by-workshop basis, prioritized according to your current goals and objectives. Over time, these individual upgrades can be seamlessly integrated into a centralized system, enabling comprehensive management of plant operations both locally and remotely. By applying the Pareto principle, where 20% of the issues typically cause 80% of the challenges, you can focus on addressing these high-impact areas first. Once these critical upgrades are in place, additional automation and enhancements can be carried out as needed, based on your specific requirements and priorities. This phased, results-driven strategy not only ensures a smooth transition to Industry 4.0 but also provides a cost-effective and efficient framework for achieving sustainable manufacturing excellence. It empowers you to optimize processes, reduce downtime, and increase productivity while adapting to the evolving demands of modern industrial standards.
3.0 End Note
The information provided outlines the cost efficiency and effectiveness of IoT (Internet of Things) based industrial automation, especially when compared to the continuous expansion of traditional PLC and SCADA systems. While adopting an IoT-driven approach may seem like a divergence at first, it offers seamless integration with your existing MES (Manufacturing Execution System), ensuring compatibility and future scalability. Moreover, this path empowers you to build your own customized MES system, free from the limitations of traditional systems, where device and system interoperability often pose significant challenges. With IoT, you gain complete flexibility, ensuring that all devices and systems communicate effortlessly, eliminating current industry roadblocks. If you're ready to explore how IoT solutions can transform your operations and deliver sustainable advantages, we invite you to contact us.